FLAT EARTH REFLECTIONS (Robert Bassano) - PLANATE VERITAS SCIENCE CALL DAY: SOHO & DISCOVR SATELLITE TEAM MANAGERS
Dear Robert Bassano (FLAT EARTH REFLECTIONS aka PLANATE VERITAS),
Unfortunately, in your video you make several claims that are not supported by scientific fact, or logical thinking...
The L1 Lagrange point is 1-million miles FROM THE EARTH, and 92-million miles FROM THE SUN.
So why are you talking about a satellite burning up?
That simply will never happen at L1.
When you interview folks on the phone from NASA or other agencies, you should really get there permission to tape the conversation first. But you are not doing that. Therefore, you are misrepresenting the intent of your call.
The more videos I watch, the more I find it harder and harder to believe that you have been accepted and are actually going to the Columbia University Applied Physics MS program.
Your current physics knowledge seems to be at a high school level (if that).
Fact check = You FAIL
You don’t understand the difference between heat and temperature.
Heat vs. Temperature
1. Heat and temperature are not the same thing.
2. Heat energy is the total kinetic energy of the atoms of a substance.
3. Temperature is the average kinetic energy of the atoms of a substance.
4. Each atom has a certain amount of kinetic energy. This energy fluctuates due to the many collisions with other atoms. However, when two atoms collide transferring kinetic energy from one to the other, no kinetic energy is lost. If the amount of kinetic energy for each atom is added up then you would have a value representing the heat energy of that collection of atoms. It follows that the more atoms which are counted, the greater the heat energy will be.
5. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of those atoms. The result of this difference between heat and temperature causes the number of atoms measured to play a major role in understanding how much heat energy an object has at a particular temperature.
6. For example, if two glasses of water are left out on the table, one completely full and the other exactly half full, they will eventually both come to room temperature, about 21°C. They may have the same temperature, but the full glass has twice the heat energy of the half full glass. Because the full glass has twice as many molecules each carrying some heat energy (or kinetic energy) the full glass has more heat at the same temperature.
7. The higher the temperature the faster the atoms move.
8. Large objects can have a kinetic energy and temperature which are distinctly separate things. For example, a baseball sitting still has no kinetic energy, but its atoms are moving, so they have kinetic energy. Because the temperature of a substance is due to the average kinetic energy of its atoms, the ball does have a temperature. Depending on how many atoms it takes to make up the ball, it has a certain amount of heat energy (the total energy of the atoms comprising the ball).
9. Because temperature is a function of the average kinetic energy of the atoms, the lowest possible temperature would be when the atoms stop moving, therefore having no kinetic energy. Because there is a lowest possible temperature, it would make sense to use a temperature scale that starts at zero. This temperature scale is called the Kelvin temperature scale and zero Kelvin is a special temperature called absolute zero (when all atomic motion is stopped).
10. An atom, however, can't separate kinetic energy from heat energy. For atoms they are one and the same thing. A bunch of atoms sitting still have no kinetic energy, no heat energy, and would have zero temperature (on the Kelvin temperature scale).
11. In summary:
• For an atom Kinetic Energy = Heat Energy
• For a substance Heat Energy = Total of all the Kinetic Energies of its atoms
• For a substance Temperature = Average Kinetic energy of its atoms
*
Fact check = You FAIL
DSCOVR positioning at L1 HAS NOTHING TO DO WITH TEMPERATURE. as you claim.
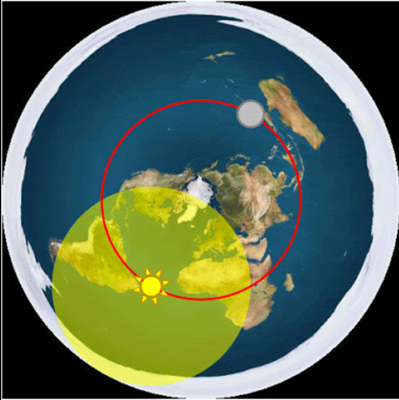
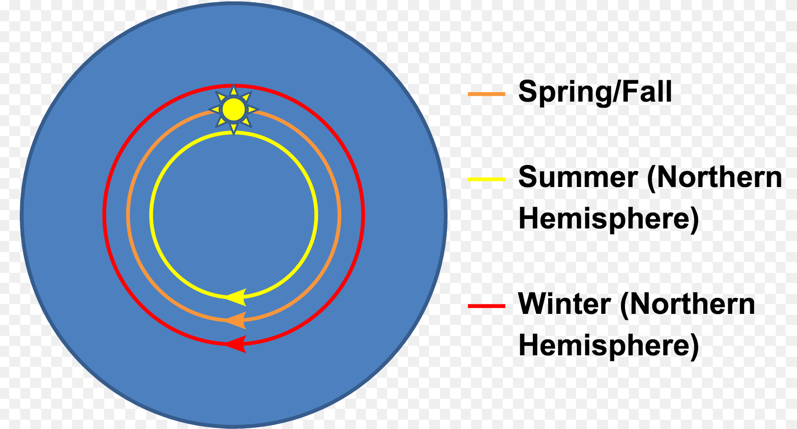
Your claim at time mark 22:20, “I think I know why they are a million miles away, because that’ the safe zone. Any closer, everything is melted.”
Why is DSCOVR at a Lagrange point? It’s all about gravity (Sun & Earth) and orbit stability.
In celestial mechanics, the Lagrangian points are positions in an orbital configuration of two large bodies where a small object affected only by gravity can maintain a stable position relative to the two large bodies. The Lagrange points mark positions where the combined gravitational pull of the two large masses provides precisely the centripetal force required to orbit with them.
Lagrange point diagram…
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_objects_at_Lagrangian_points#/media/File:Lagrange_very_massive.svg
Video at..
(https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NYjOyS8q0SY)
- - -
Update: February 5, 2022
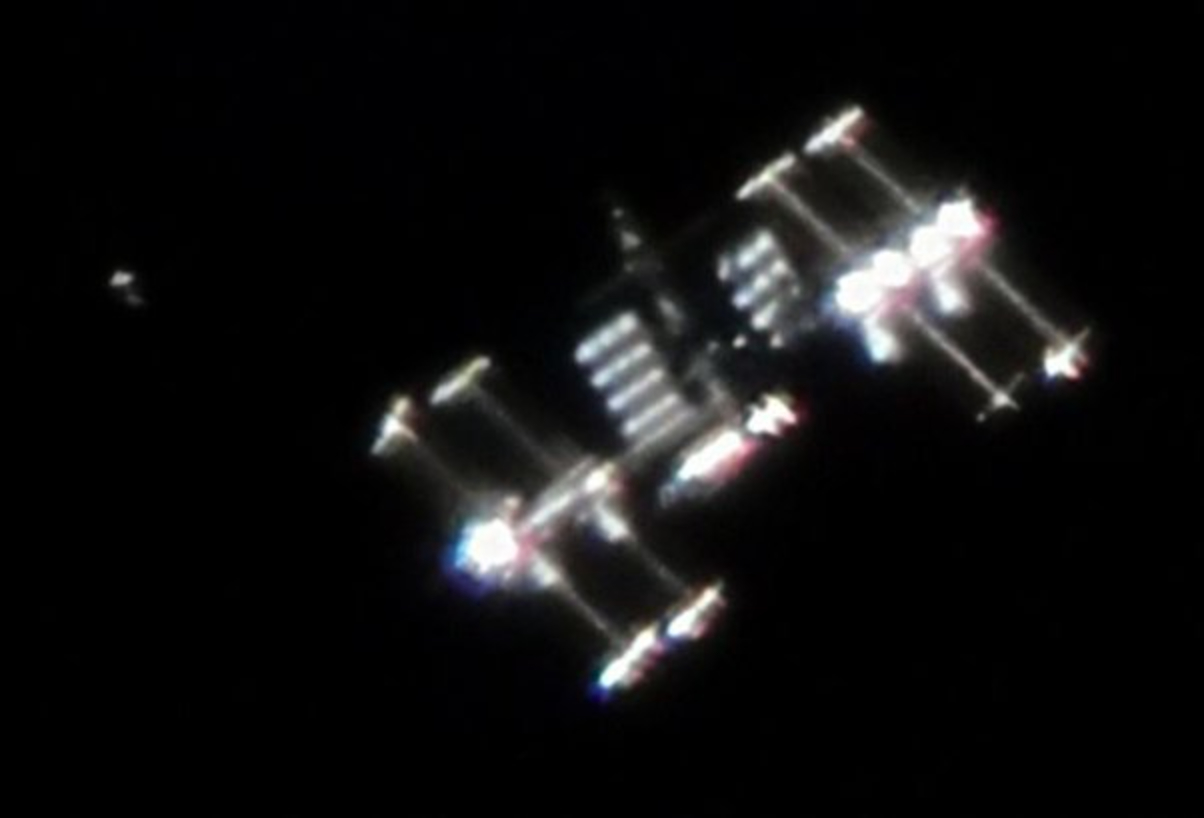
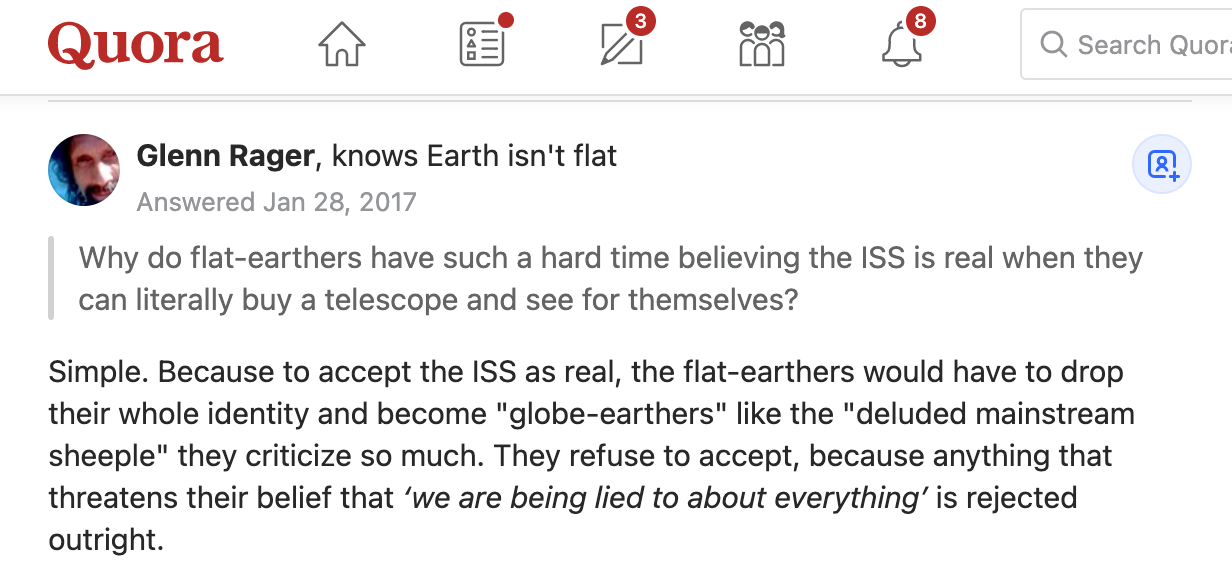
Why do flat-eathers have such a hard time believing the International Space Station (ISS) is real when they can literally buy a telescope and see fo themselves?
https://www.quora.com/Why-do-flat-earthers-have-such-a-hard-time-believing-the-ISS-is-real-when-they-can-literally-buy-a-telescope-and-see-for-themselves
-
Published on – October 21, 2016
Discussion at - https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC7ipUKERU0tzYFxALJBli4A/discussion
Video at - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NYjOyS8q0SY
Our home page all articles - http://flatearthlunacy.com
kind regards, JonahTheScientist
- - - - - - - - - -

- - -

- - - - - - - - - -

- - -

- - - - - - - - - -