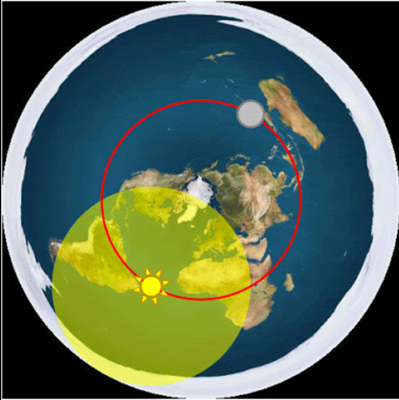
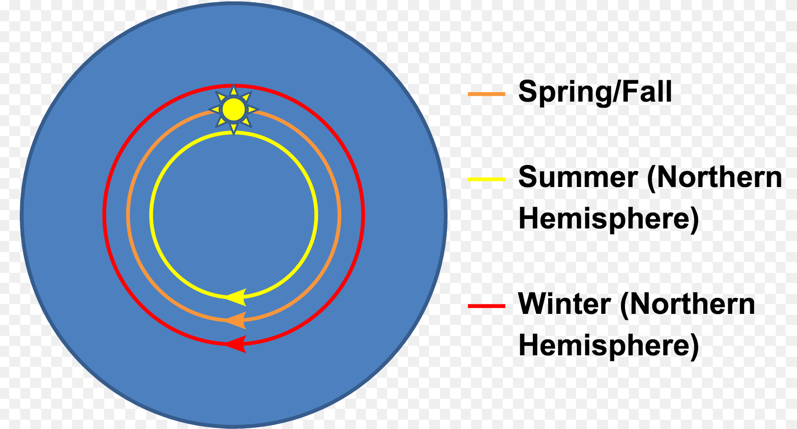
FECORE - Lake Ijssel Netherlands Laser Test FAIL. Peer Review summary -> How atmospheric temperature inversion / ducting layer boundaries, over the water horizon, always yield erroneous and misleading results.
Dear Readers,
Update: August 2019:
The truth finally comes out of Mike Cavanaugh validating all we have said in this and our other articles on the FECORE laser test.
As Mike Cavanaugh finally explains in this August 2019 interview with Sly Sparkane, the goal of the laser test was to hit the distance target. Nothing else.
Our note: That does not prove the earth is flat. The laser can be aimed up/down and left/right. Point it above the horizon line any way you want just to get the laser light seen at the target location.
Aimed and traveling over the horizon the laser beam is refracted by the atmosphere and subject to other thermal distortions, before its ever widening beam (laser beam divergence) makes it to the distant target.
This only proved that the laser was bright enough to be seen from those distances. Nothing else.
Sly Sparkane says,
“What was the ultimate goal of the test? Was it to see the laser at the other end or was it to hit a target?”
Mike Cavanaugh says,
"to hit a target..."
Sly Sparkane says,
“and did you hit a target…”
Mike Cavanaugh says
“yes…”
Sly Sparkane says
“at 22 kilometers?”
Mike Cavanaugh says,
“at 20 and 26 or 27 or 29 now…”
This is FECore (MIRRORED), by Flat Earth Reset 3
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V67XR5Xkhd8
Update: October 2019:
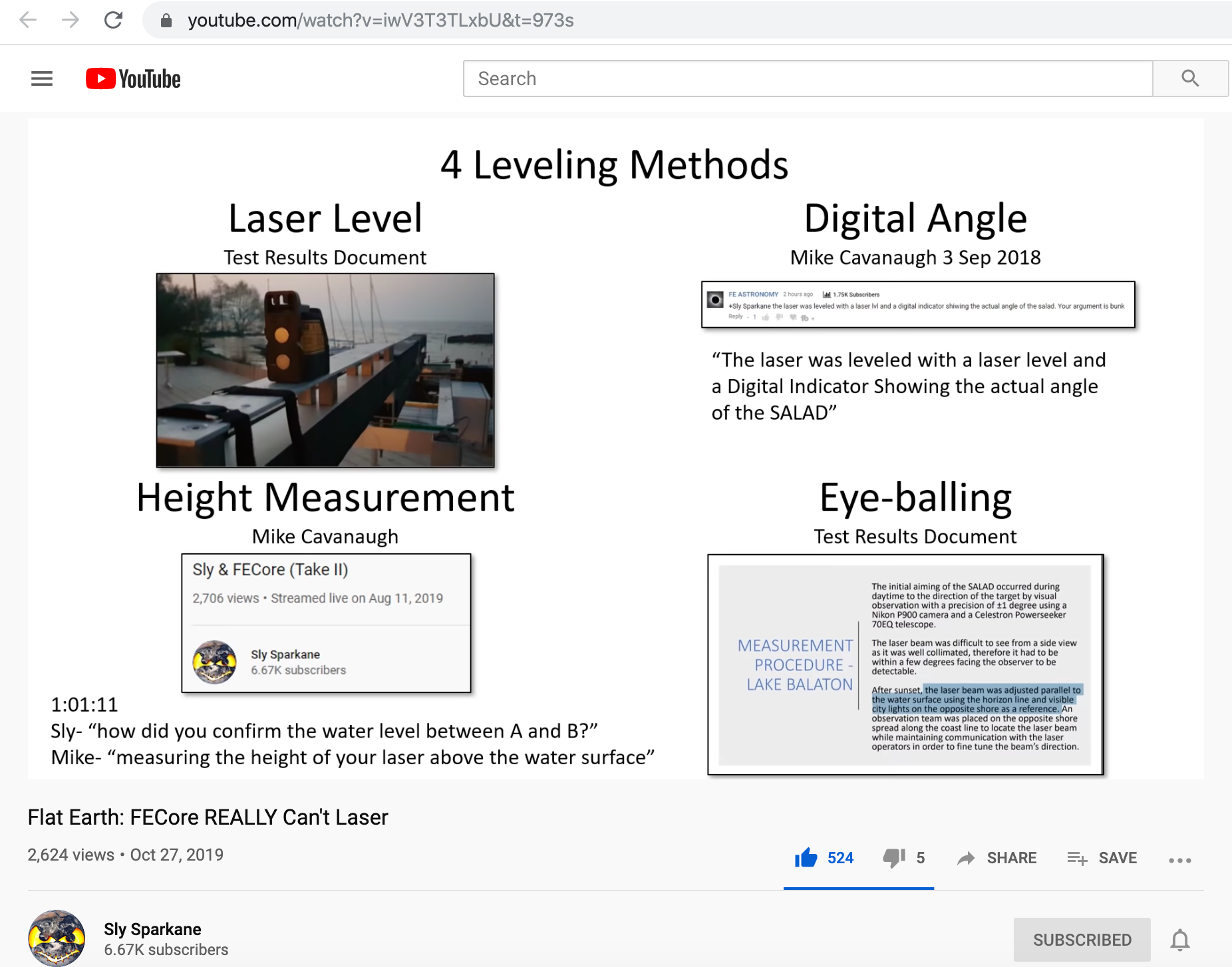
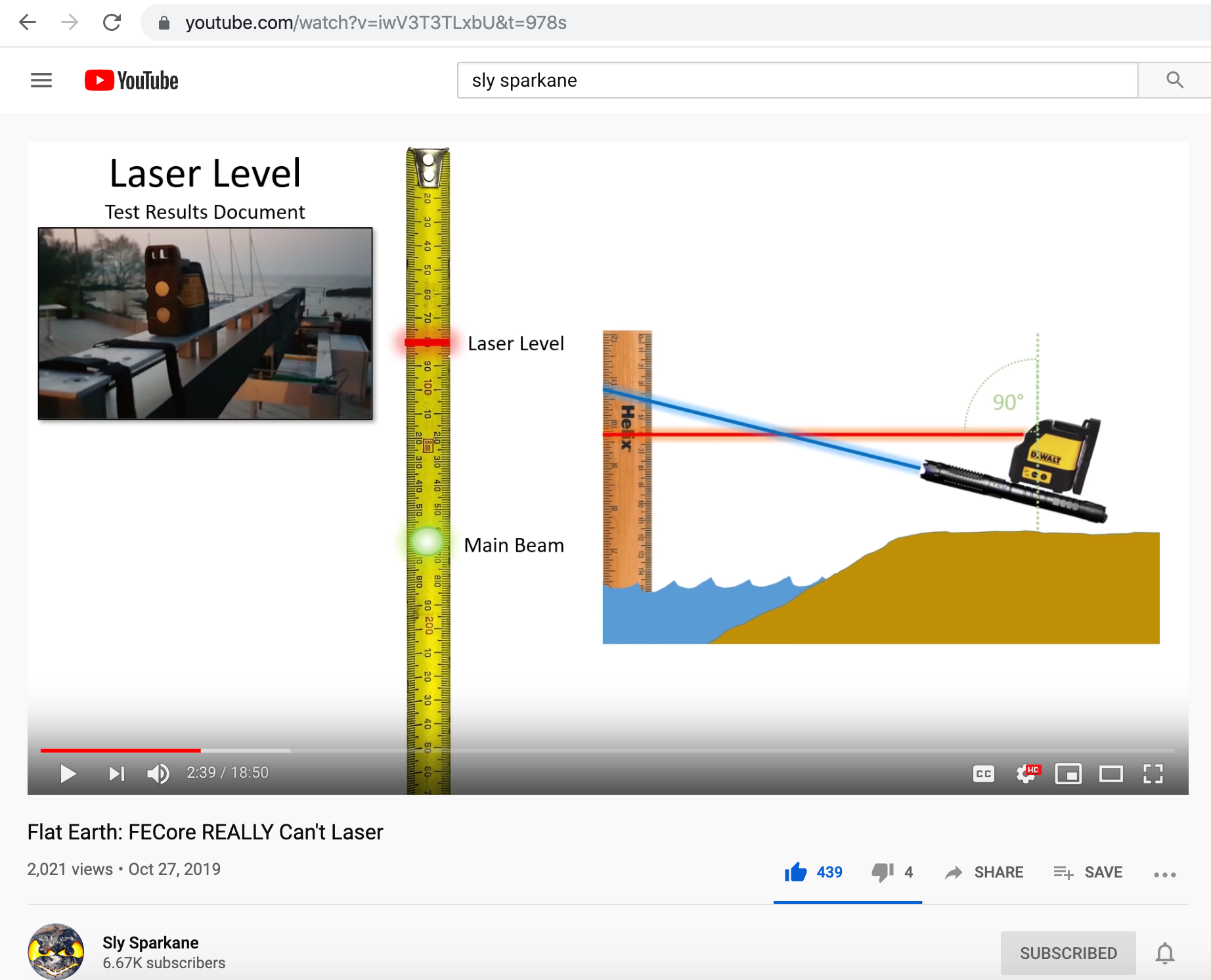
The following video by Sly Sparkane validates the main xx points that we presented 18-months ago.
Flat Earth: FECore REALLY Can'r Laser, by Sly Sparkane
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iwV3T3TLxbU&t=973s
-
-
-
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Published on – June 14, 2018
Abstract:
1. No attempt was ever made to measure Earth flatness.
During the entire course of the experiment they did not use any of the standard Geodetic survey tools; such as an internationally approved Theodolite/Auto level, GPS tracker, level staff, ranging rod, retro-reflector and surveyor’s tripod.
They did not place level staffs or sighting targets at various marker points along the Lake Balaton shoreline, to demonstration progressive tracking of Earth flatness over length.
They did not stake laser reflectors at various locations along the shoreline, and target them with a laser beam to demonstrate that the beam is truly pointed parallel to the water's surface over distance. That is a primary requirement to corroborate flatness.
2. All efforts were directed toward showing that there is no Earth curvature.
The FECORE team did however, attempt thru observations, to imply "proof by contradiction."
Proof by contradiction is a form of indirect proof, that establishes the truth or validity of a proposition. It starts by assuming that the opposite proposition is true, and then shows that such an assumption leads to a contradiction.
The error in this type of approach is the "assumption" that the Earth can only have two possible valid shapes - either flat or spherical. Attempting to prove that the Earth is not spherical, does not authenticate that the Earth is flat. And other flat Earth supporters willingly testify that the Earth is concave, convex, or undoubtedly a flat plane with as yet unmeasured total dimensions
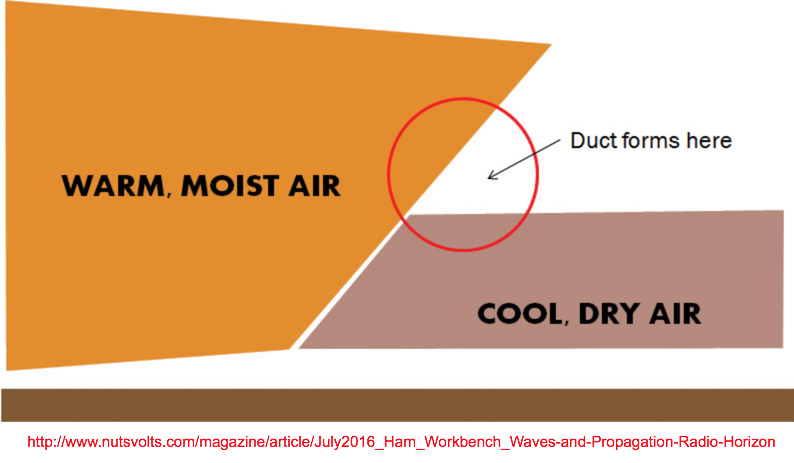
3. In order to avoid confusing and contestable results due to atmospheric effects - all laser experiments should only be conducted within the observable horizon.
Laser height above the water line:
1.5 meters = Test over water to a distance of (4.4 kilometers / 2.73 miles)
5 meters = Test over water to a distance of (8 kilometers / 4.97 miles)
10 meters = Test over water to a distance of (11.3 kilometers / 7 miles)
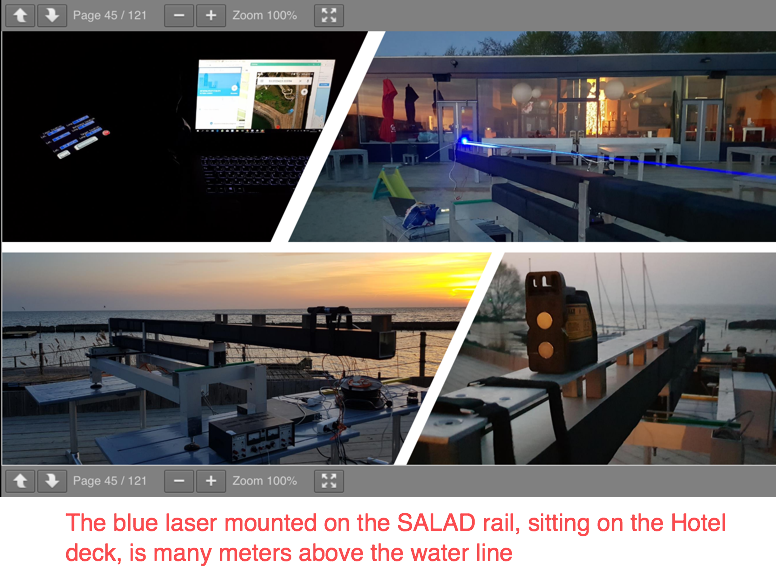
13 meters (hotel terrace position of laser) = Test over water to a distance of (12.9 kilometers / 8 miles)
20 meters = Test over water to a distance of (16 kilometers / 9.94 miles)
30 meters = Test over water to a distance of (19.6 kilometers / 12.18 miles)
The below mentioned phenomena radically change light propagation direction and behavior:
turbulence (rising and falling air currents, and the offshore breeze that all sailors know about)
thermal layer ducting
thermal boundary layers
thermal blooming
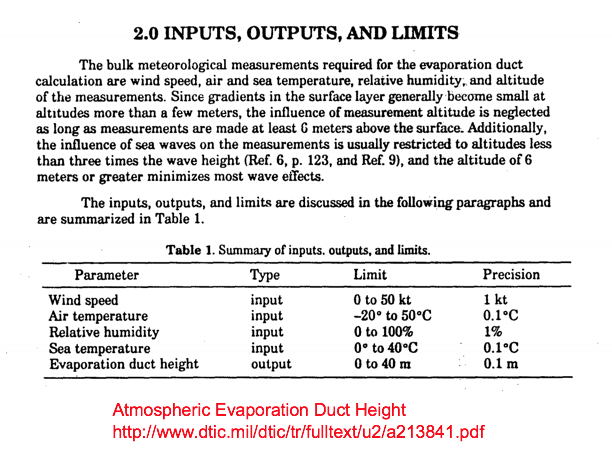
evaporation duct height
atmospheric looming, sinking, towering & stooping
inferior mirage, superior mirage, and Fata Morgana
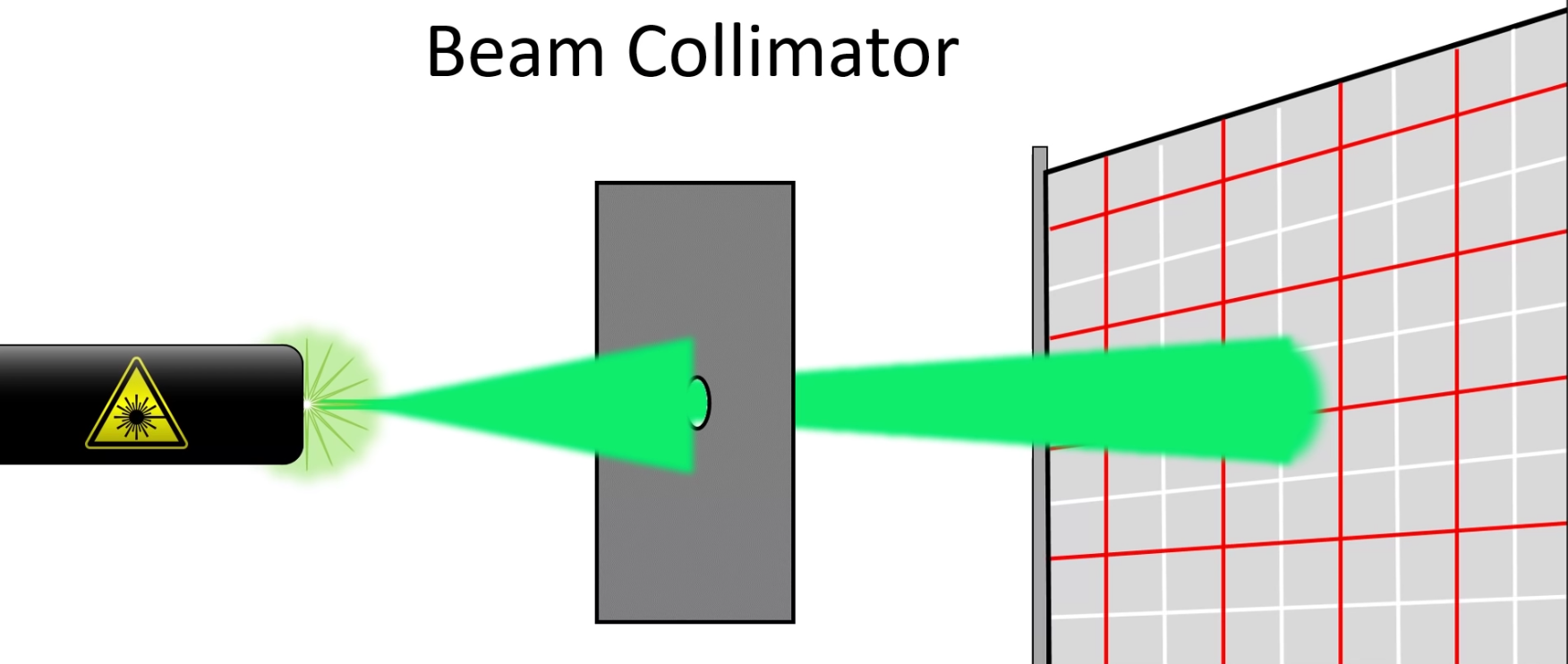
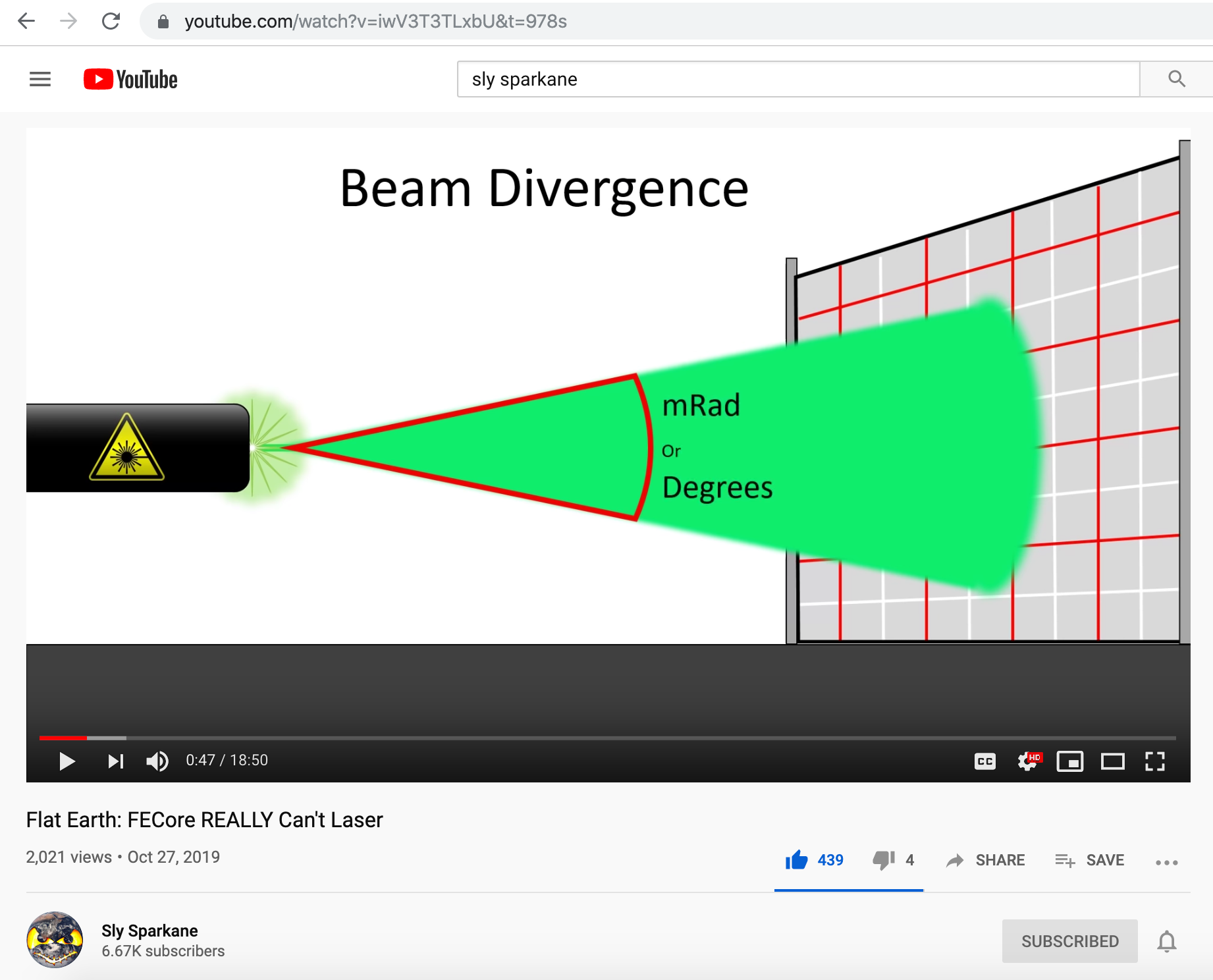
4. The laser beam (green & blue) diameter is on the order of millimeters, yet the resulting observed light images observed at the target locations are meters upon meters wide.
5. Given the small beam at the source, diffraction and natural beam divergence produces a large (order of meter or meters) beam at the detector.
6. Regardless of atmospheric refraction/ducting, this large beam is essentially a plane wave, large enough to reach from near the ground to the location of the detector (eye or camera) at the various test distances on it's own.
7. Whether by eye or camera, a small portion of this plane wave is sampled and appears as a spot in the camera. This spot is sometimes distorted by small scale aberrations in the atmosphere or scatter of diffracted light off the surface of the water.
8. While they didn't show it or do it, they would have seen the same spot as they moved the detector up and down vertically (sampling different parts of the beam). Please note that to find the beams actual location would require finding the center of the beam (the brighter center). If they had done that, you could have drawn conclusions about the extent of refraction/ducting).
9. We will show below how to properly conduct an over-the-water laser distance experiment.
10. Lighthouse or bright lamp testing could also have been used to obtain reliable results.
Summary:
Basically, this experiment (if they had scanned vertically) suggests that diffraction is real and doesn't show whether the earth surface curves or not.
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Measurement 1:

-

-

- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Measurement 2:
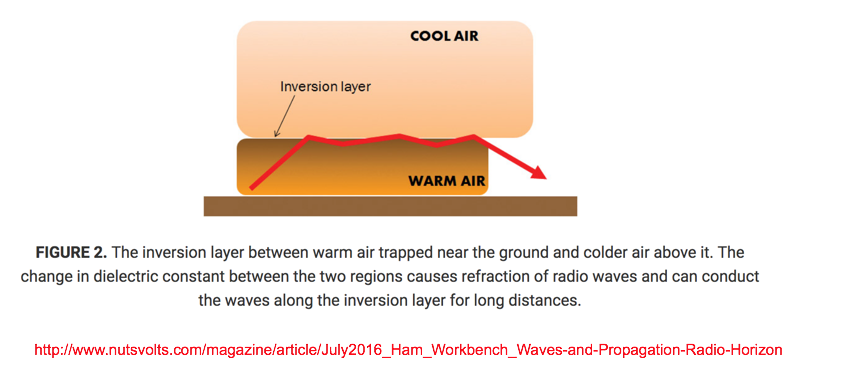
Due to a normal temperature gradient found in the atmosphere, light rays are bent 1/5 or 1/6 the Earth’s curvature.
With a temperature inversion (increase or decrease) of 6.3o F per 100-feet, the curvature of a light ray is of the same order as the curvature of the Earth.

- - -

-

-
-

-

- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
FECORE - Lake Ijssel Neterlands laser pictures presented...
Measurement 3:

-
-

-

-



-

-

-

- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
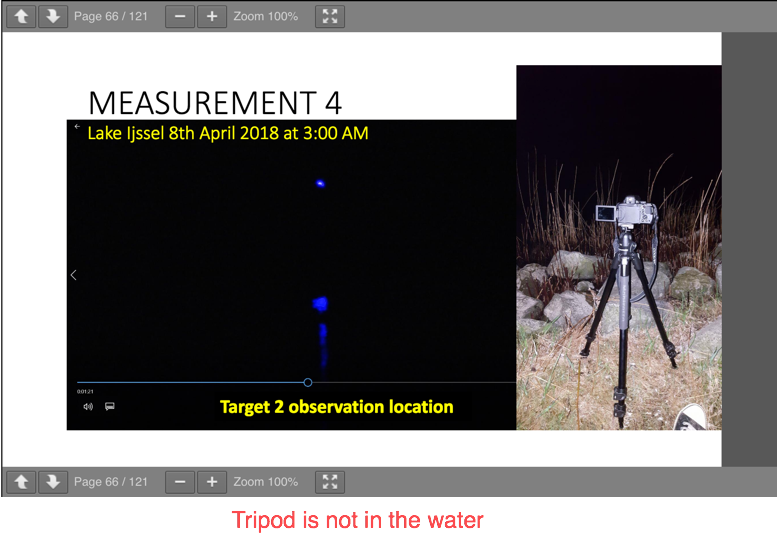
Measurement 4:
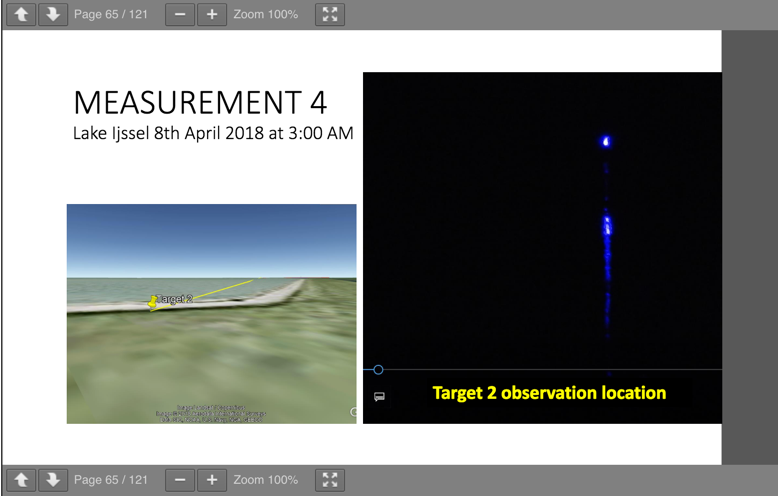
-

-
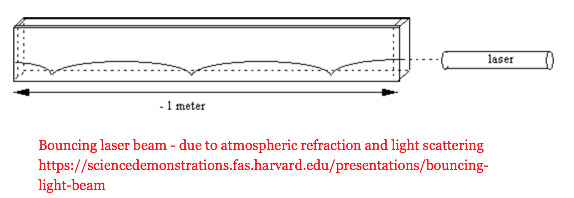
Diffused light due to waves causes a reflected skipping effect...

Light skipping across water wave...
-
-

- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Measurement 5:

-
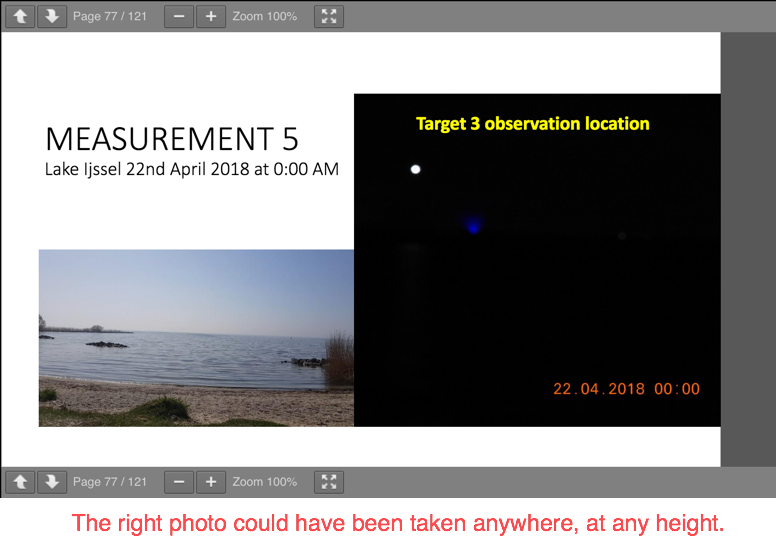
-

- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Measurement 6:

-

- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Measurement 7:
-
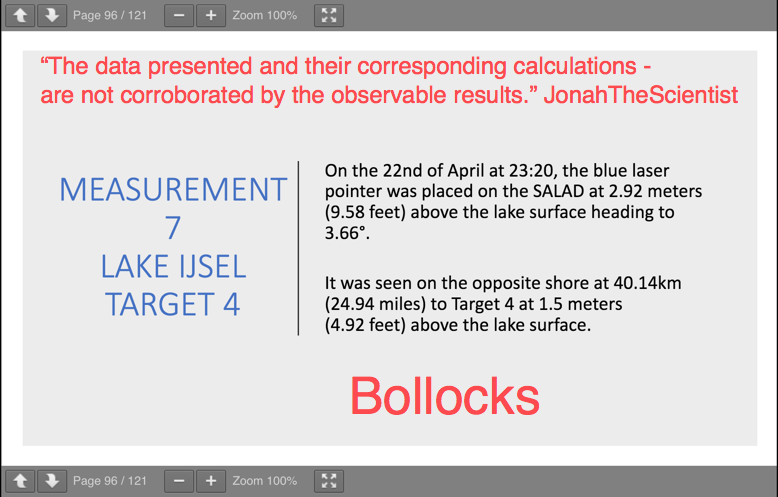
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Fecore conclusion:
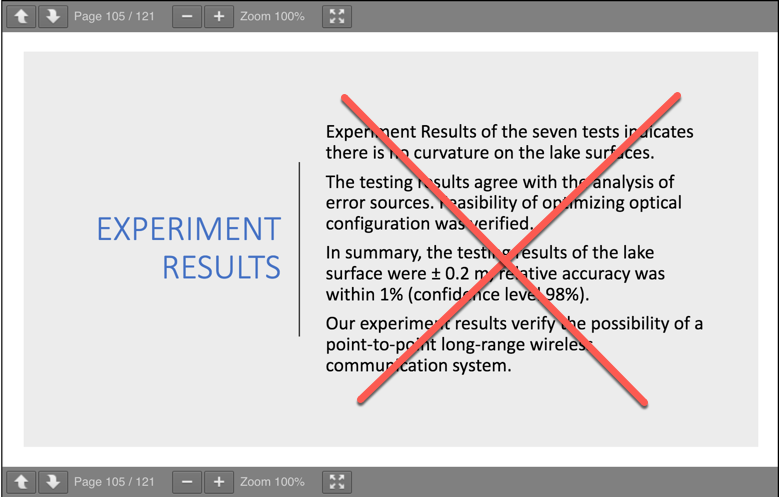
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
1. No attempt was ever made to measure Earth flatness.
More explanation:
None of these standard surveying measuring tools were ever used by FECORE in their experiments. If they had, earth curvature would have been proven right off the bat.
.
Setup standard height markers at various distances, in ice or on land...
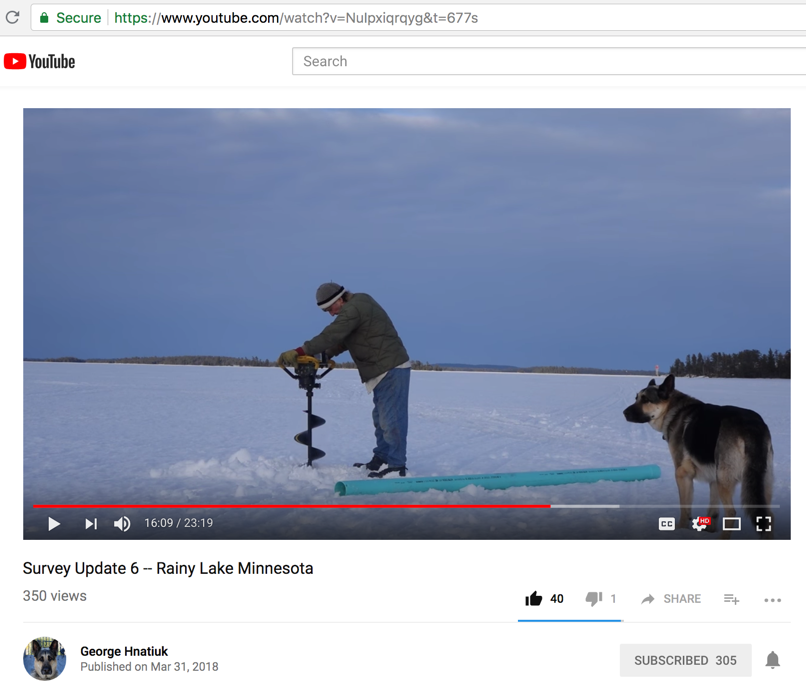
Video here - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NuIpxiqrqyg&t=677s
-

-
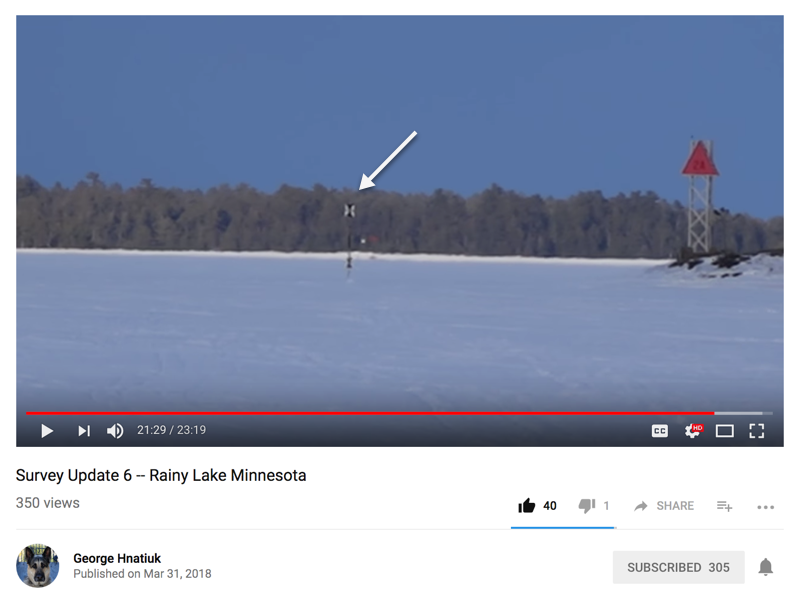
-
View all markers with the auto level to determine elevation and curvature over distance. It's best to place all markers within the same line of sight. No more than 1,500 yards' maximum separation distance between markers is needed, so that atmospheric inversion and refraction do not play any role in the measurement.

Easy done deal with no room for debate!
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
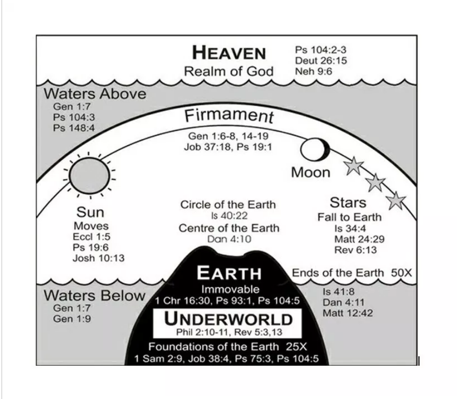
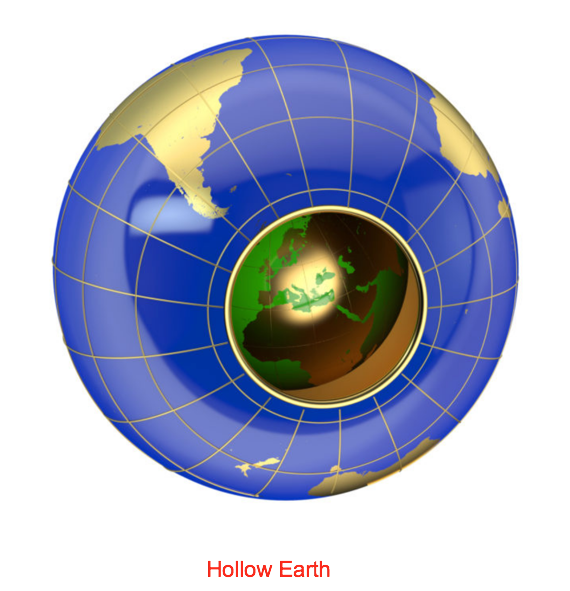
2. All efforts were directed toward showing that there is no Earth curvature.
More explanation:
Trying to prove that the Earth has no curvature does not prove that the Earth is flat. That's because various peoples and cultures of the world attest that the Earth really is ...

-

-

-

-

-
-
-

-

-

-

etc.
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
3. In order to avoid confusing and contestable results due to atmospheric effects - all laser experiments should only be conducted within the observable horizon.
More explanation:
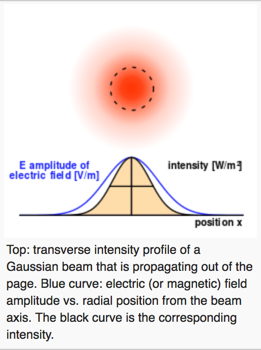
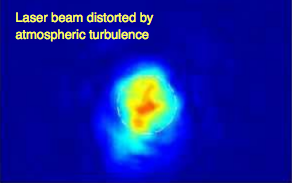
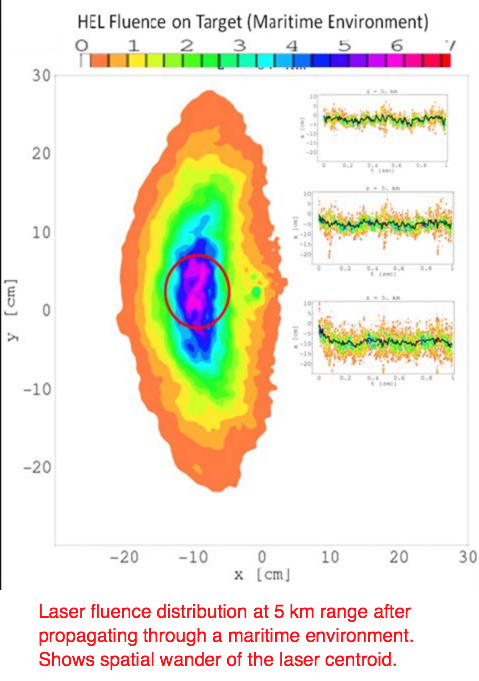
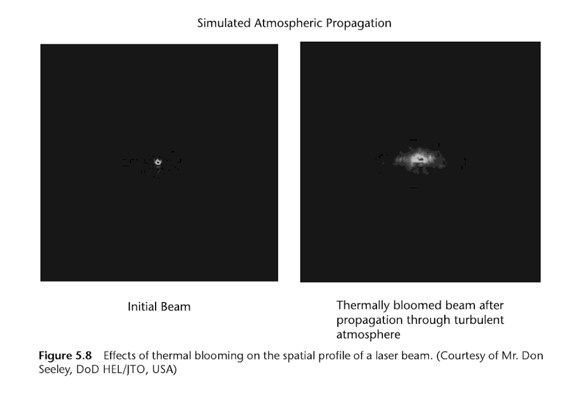
Here is what a laser beam looks like (normal Gaussian distribution) when there is no interference for external effects. It's obvious that NONE of the laser images at the target site shown by FECORE look like this.

-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
4. The laser beam (green & blue) diameter is on the order of millimeters, yet the resulting observed light images observed at the target locations are meters upon meters wide.
More explanation:
Limitations for the Focusing of Laser Beams (assuming no atmospheric or other type of distortion)
Laser beams can be used for transmitting optical energy to rather small spots or with low beam divergence over large distances. However, there are limitations to this, which involve the optical wavelength, the beam quality and the transverse size of the used focusing or collimation optics.
If a laser beam is focused to a spot beam waist with beam redius w0, it exhibits a certain beam divergence angle which is inversely proportional to the waist beam radius and proportional to the optical wavelength in the M2 factor:
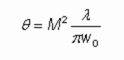
The used focusing optics must be able to handle that amount of beam divergence; a limitation for that results from the limited numerical aperture of the optics. Also, if the focus has to have a large distance from the focusing optics and/or the waist beam radius is small or the beam quality is low, the beam radius in the focusing optics will necessarily be quite large. A correspondingly large open aperture of the optics is required. Such factors can in practice set a lower limit to the achievable beam radius in the focus, or an upper limit to the tolerable M2 factor of the beam:
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
5. Given the small beam at the source, diffraction and natural beam divergence produces a large (order of meter or meters) beam at the detector.
More explanation:
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
6. Regardless of atmospheric refraction/ducting, this large beam is essentially a plane wave, large enough to reach from near the ground to the location of the detector (eye or camera) at the various test distances on it's own.
More explanation:
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
7. Whether by eye or camera, a small portion of this plane wave is sampled and appears as a spot in the camera. This spot is sometimes distorted by small scale aberrations in the atmosphere or scatter of diffracted light off the surface of the water.
More explanation:
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
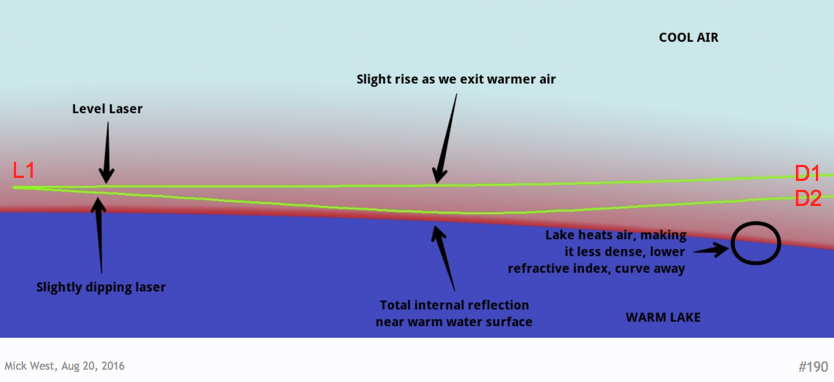
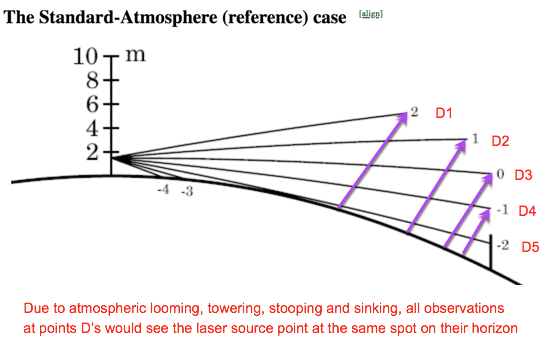
8. While they didn't show it or do it, they would have seen the same spot as they moved the detector up and down vertically (sampling different parts of the beam). Please note that to find the beams actual location would require finding the center of the beam (the brighter center). If they had done that, you could have drawn conclusions about the extent of refraction/ducting).
More explanation
A camera at position D1 or D2, which are clearly at different heights above the surface, will still see the laser source at the SAME place L1 on their horizon.
-
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
9. We will show below how to properly conduct an over-the-water laser distance experiment.
More explanation:
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
10. Lighthouse or bright lamp testing could also have been used to obtain reliable results.
More explanation:
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
SUMMARY:
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Invitation to Peer review:
-

-

- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
.